Essential Elements Of A Contract
Contract
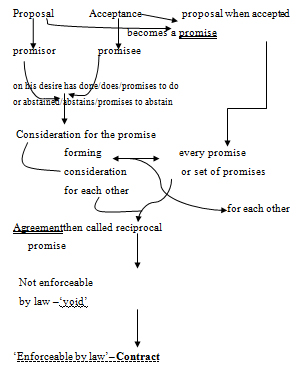
Definition: section 2(h)[1] defines contract as an agreement enforceable by law:
- Agreement is defined in section 2(e)[2] as every promise and every set of promises, forming the consideration for each other.
- A promise is when a proposal is accepted it becomes a promise as defined in section 2(b)[3].
- The person who makes the proposal is called the promisor and the person accepting is called the promisee as defined in section 2(c)[4].
Thus, the definition of contract can be compiled as follows:
When a proposal made by the promisor is accepted by the promisee and a promise
is established between them forming a consideration for each other this becomes
an agreement and when this agreement is enforceable by law it becomes a
contract.
Notes:
- An agreement without any consideration is void.
- Agreement can be of many kinds. It can be commercial, domestic or social, but only commercial agreements are enforceable by law as there is a valid consideration in commercial agreements but not in domestic and social agreements.
- There should be an intention of creating legal relationship in any agreement.
Introduction to contracts - Section 2
Essential elements of a contract
The essential elements of a contract can be classified into two categories i.e. substantive elements and procedural elements
1. Substantive elements
|
2. Procedural elements
|
Offer (proposal):
Section 2(a)[5] defines proposal/offer as:
When one person signifies to another his willingness to do or to abstain
from doing anything, with a view to obtaining the assent of that other to such
act or abstinence, he is said to make a proposal.
Every contract starts from an offer. Without an offer there can be no acceptance
and then no agreement and then no contract. Thus offer becomes an essential
element for a contract.
Essentials of a valid offer:
- Intention to obtain the acceptance.
- Intention to create legal relationship.
- The offer must be certain.
- A valid offer should not contain any term, the non compliance of which leads to acceptance.
- The offer must be communicated.
Communication of offer:
As it is essential for an offer to be communicated to be valid, section 4[6] of
Indian Contract Act states that the communication of the offer/proposal is
complete when it comes to the knowledge of the person to whom it is made.
Therefore until and unless the information of the proposal reaches the person to
whom it is made, the offer is not considered valid. And if the knowledge of the
offer does not reach the other party then how will the other party accept the
offer and until there is no acceptance of the offer, there will be no agreement
between the parties. And without agreement and its enforceability by law, a
contract cannot be completed.
Thus completion of communication of offer becomes essential for establishment of
a contract between any two or more parties.
Acceptance:
Section 2(b)[7] defines acceptance as:
When the person to whom the proposal is
made signifies his assent thereto, the proposal is said to be accepted.
Once the offer is extended, it is in the hands of the offeree (the person to
whom offer is made) to either accept or reject the proposal/offer.
Without acceptance of the offer there can be no agreement (whose enforceability
by law results in a valid contract), thus acceptance is another essential
element for a contract.
Communication of acceptance:
Section 4 states that the communication of acceptance is complete:
- As against the proposer, when it is put in a course of transmission to him, so as to be out of the power of the acceptor;
- As against the acceptor, when it comes to the knowledge of the proposer.
For example,
A proposes, by letter, to sell a house to B at a certain price. B accepts A's
proposal by a letter sent by post.
The communication of the acceptance is complete,
as against A, when the letter is posted;
as against B, when the letter is received by A.
Any offer will not be considered to be accepted until and unless the knowledge
of acceptance reaches the offeror. Thus, communication of acceptance becomes an
essential element in order to establish a contract between two or more parties.
Meeting of minds:
The meeting of minds in contract law refers to the moment when both parties have
recognized the contract and agreed to enter into its obligation. This is also
called Mutual assent or consensus ad idem.
As a contract can be voided if it is formed by undue influence, fraud,
misrepresentation, thus mutual assent is essential.
Consideration:
Section 2(d)[8] defines consideration as:
When at the desire of the promisor,
the promisee or any other person has done or abstained from doing, or does or
abstains from doing, or promises to do or to abstain from doing, such act or
abstinence or promise is called a consideration for the promise.
Something of value must be exchanged in order to have a valid legal agreement as
any agreement without consideration is void. Thus if there will be no
consideration then the agreement will be void and it will not be enforceable by
law and there will be no contract.
Therefore consideration is must for a contract.
Exception: section 25:
there is an exception for following cases where agreement without consideration is valid:
- If the agreement is expressed in writing and registered under the law for the time being in force, and is made on account ofd natural love and affection between parties standing in a near relation to each other; or
- It is a promise to compensate, wholly or in part, a person who has already voluntarily done something for the promisor, or something which the promisor was legally compellable to do; or
- It is a promise, made in writing and signed by the person to be charged therewith, or by his agent generally or specially authorized in that behalf to pay wholly or in part a debt of which the creditor might have enforced payment but for the law for the limitation of suits.
Capacity to contract:
Capacity simply means competence or ability of the parties to come into a
contract. A capable person is the one who is allowed /qualified to enter into a
contract.
Section 11[9] of Indian Contract Act defines who are competent to contract:
- Major person
- Person with sound mind (section 12 defines unsound mind)
- Person not disqualified by law
- Convicts
- Alien enemy
- Insolvent
- Married women (with respect to her husband's property)
- Corporations
A person who is not capable cannot come into any contract, thus capacity to
contract is an essential element for a contract.
Legality:
As section 2(h) defines contract as - ‘An agreement enforceable by law', the
legality becomes the most important element of a contract. One cannot enforce a
contract which is unlawful.
Also, every agreement of which the object or consideration is unlawful is void.
Section 23[10]defines what considerations and objects are lawful, and what not
-Should not be forbidden by law; or Should not defeat provisions of any law; orShould not imply injury to the person or property of another; or The court
should not regard it as immoral or opposed to public policy.
Thus, legality is an essential element for a contract.
Valid Contract
A valid contract should have all essential elements including offer, its
communication, meeting of minds, acceptance, communication of acceptance,
consideration, capacity, legality.
The two main essential elements of a contract are:
- An Agreement and
- Enforceability of this agreement by law
Substantive Elements Procedural Elements
| Offer Acceptance Agreement Consideration |
Communication of offer and acceptance and meeting of minds |
Substantive Elements
| Capacity to contract Legality | Enforceability by law |
Note: The procedural elements of a contract play as equal role as the
substantive elements for a contract.
The substantive elements will not be valid until and unless the procedural part
is complete.
Example of a valid contract
These essential elements for a contract can be more clearly demarcated through a
situation in which there is a commercial contract between two parties for
selling and buying a motor bike at the cost of Rs 100000.
A sends a letter to B asking him to sell his motor bike at
Rs 100000 on February 8 - offer.
The letter is received by B on February 9 -
communication of offer is complete.
B agrees with free will(meeting of minds) to sell his bike to A at Rs 100000 -
acceptance.
On February 10, B sends the letter of acceptance via post. - communication of
acceptance is complete as against A as to be out of power of B,
On February 11, the letter of acceptance reaches and comes in knowledge of A. -
communication of acceptance is complete as against B.
A got the bike on February 15 and made payment to B for the bike in 3
installments - here, bike is a lawful consideration for A and Rs 100000 is
lawful consideration for B.
Here, A and B both are major and are of sound mind and are not disqualified by
law - capacity to contract.
Since a valid agreement is formed between A and B and it is also enforceable by
law, it is a valid contract including all essentials elements.
End-Notes:
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872
- Ibid
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872
- Ibid
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872
- Ibid
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872
- Ibid
- The Indian Contract Act, 1872
Written By:
Astha Dehariya, 2nd Semester B.A.Ll.B(Hons.) - Dharmashastra National Law
University Jabalpur
Law Article in India
Lawyers in India - Search By City
Popular Articles
How To File For Mutual Divorce In Delhi
How To File For Mutual Divorce In Delhi Mutual Consent Divorce is the Simplest Way to Obtain a D...
Increased Age For Girls Marriage
It is hoped that the Prohibition of Child Marriage (Amendment) Bill, 2021, which intends to inc...
Facade of Social Media
One may very easily get absorbed in the lives of others as one scrolls through a Facebook news ...
Section 482 CrPc - Quashing Of FIR: Guid...
The Inherent power under Section 482 in The Code Of Criminal Procedure, 1973 (37th Chapter of t...

Home | Lawyers | Events | Editorial Team | Privacy Policy | Terms of Use | Law Books | RSS Feeds | Contact Us
Legal Service India.com is Copyrighted under the Registrar of Copyright Act (Govt of India) © 2000-2026
ISBN No: 978-81-928510-0-6


Please Drop Your Comments